“Seeing Is Believing” - Examples of Computational Design
Mini assignment 1
Task 1
Botanical World
Spiral Phyllotaxis- the arrangement of leaves on an axis or stem

Many succulents, such as Aloe, exhibit spiral phyllotaxis. This is where the leaves or petals are arranged in a spiral pattern. This pattern often follows the Fibonacci sequence or the golden ratio. This arrangement allows for maximal exposure to sunlight and efficient growth. Nick Seewald
Images from
Zoological World
Fish Schooling
The way fish move in schools is an example of a computational-like system. Each fish follows simple rules about spacing and speed relative to its neighbors, resulting in a highly coordinated and efficient group movement. Schooling behavior is commonly mimicked in robotics and artificial intelligence swarm path planning.
“Each fish maintains a “zone of repulsion” with its neighbors where a fish automatically turns away from a neighbor in order to avoid collision.”

Images from
Environment Built by Organisms
Bowerbird Nests

Male bowerbirds build elaborate structures, known as bowers, to attract mates. These aren’t just nests, but more like stages for courtship displays. The geometric precision with which they arrange sticks, stones, and even bird-made objects is an example of aesthetic geometry in animal behavior. Just like in an algorithm, where decisions are made based on a set of rules or criteria, bowerbirds select items based on color, size, and other features.

Images from
Task 2
Beijing National Stadium (Bird’s Nest)
The stadium where the 2008 and 2022 Olympics were held is more than aesthetic. The construction of the Bird’s Nest utilized computational design for its intricate steel structure. The interlocking steel beams were algorithmically optimized to provide stability while creating an aesthetic reminiscent of a bird’s nest

Image from
Metropol Parasol- Jürgen Mayer

The Metropol Parasol’s design features undulating, organically inspired forms that are far from traditional linear or planar structures. Creating these complex geometries was made possible through computational design tools that allowed architects to explore and manipulate intricate forms. Parametric models were used to determine the best ways to achieve the desired aesthetic while also maintaining structural integrity. These models could adapt to various constraints, such as material limitations, spatial requirements, and load-bearing considerations.
Image from
PotScript: a visual grammar for sculpting with functions
This was an interesting project I saw a presentation on at last year’s ACM Symposium on Computational Fabrication. Leo McElroy and Lingdong Huang built a web-tool that can be used interactively create pottery using functions
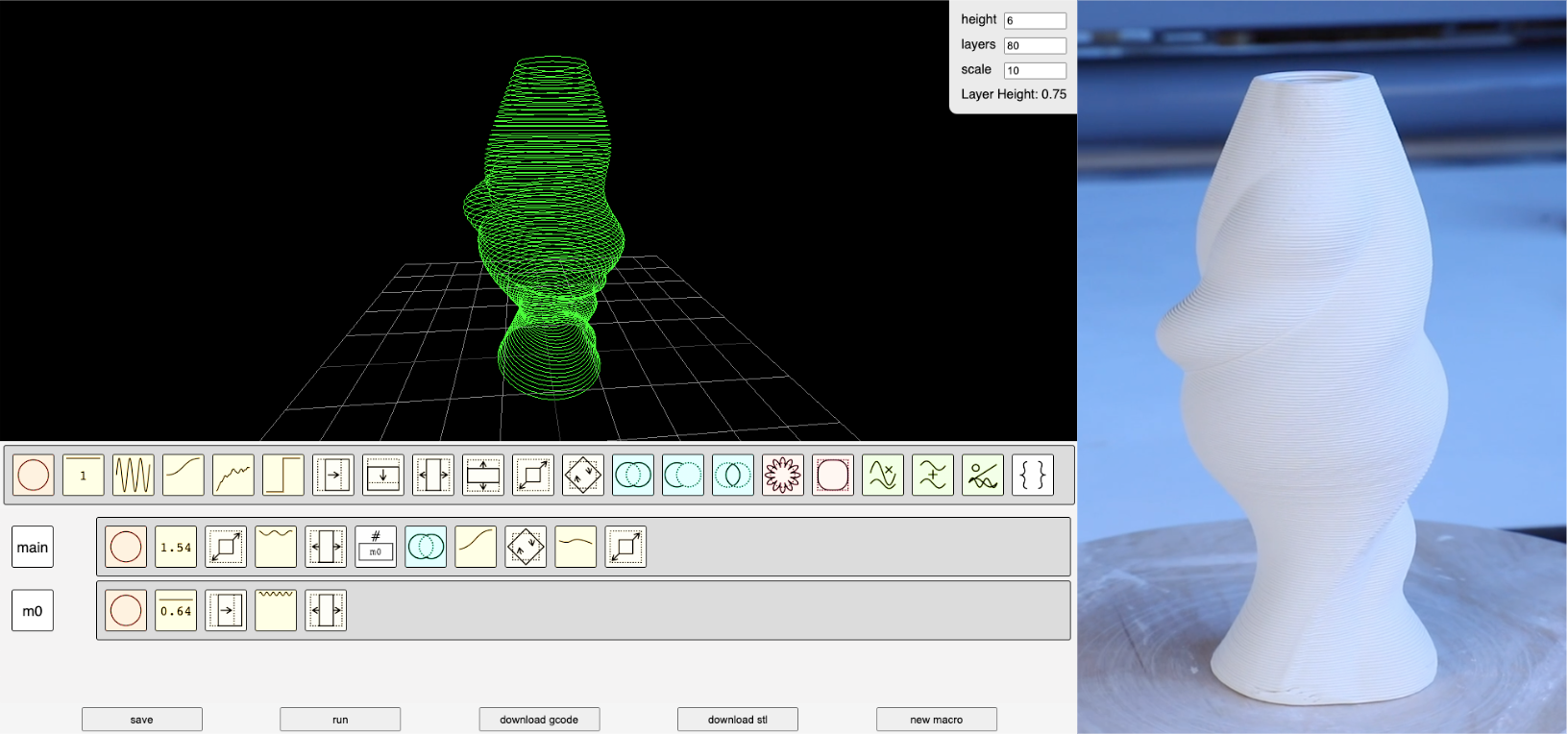
Task 3
Ezri Tarazi
Chair of the Industrial Design Program at the Technion

I listened to Ezri deliver an interesting talk on his use of 3D printing to rebuild coral reefs in the Mediterranean Sea. What’s intriguing about this project is the focus on geometry. While old ships have been sunk to create artificial reefs, they don’t always provide the healthiest environment for coral growth. Ezri’s team is exploring how various 3D-printed geometries and materials can enhance growth. More details about his work can be found in a recent paper
Nobuyuki Umetani

Associate professor at the University of Tokyo and PI of the Interactive Graphics & Engineering Lab.
Dr. Umetani operates at the intersection of design, graphics, and engineering. His laboratory has conducted some fascinating research using digital tools for garment fitting